Allosteric Regulation Is Most Similar to Which of the Following
Allosteric regulations are often end products of a biochemical pathway. All of these are advantages e.

Allosteric Regulation In Proteins Download Scientific Diagram
They may be safer as they have no effect at all unless the natural substrate is present d.
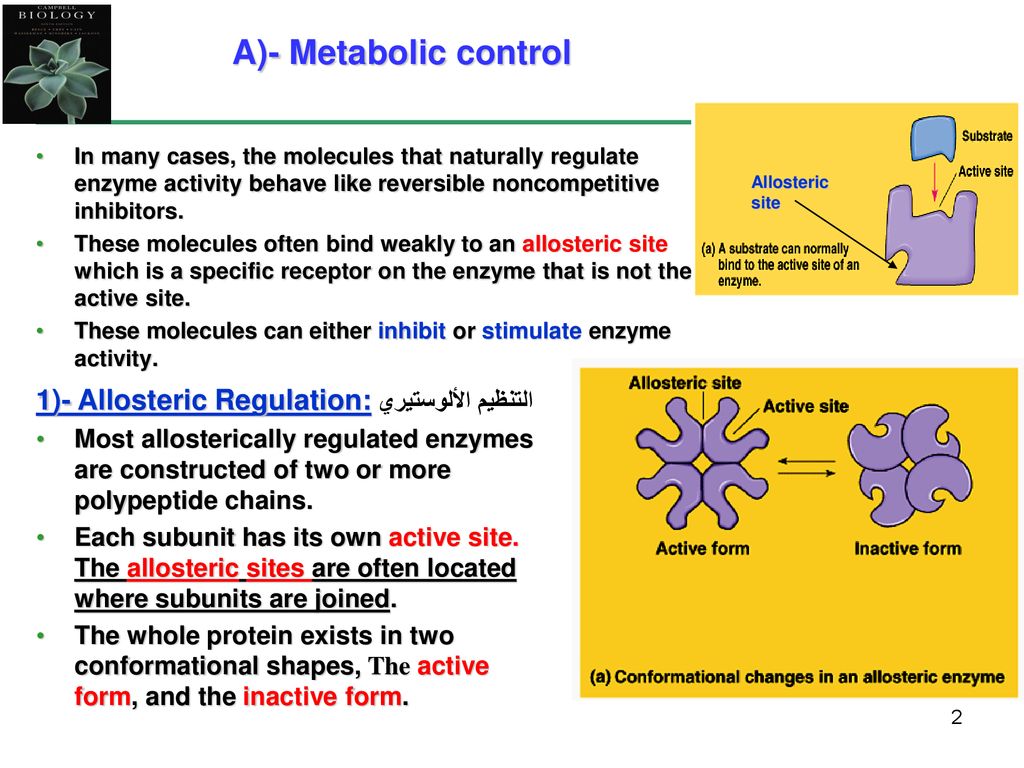
. The site to which the effector binds is termed the allosteric site or regulatory site. As pointed out on page 1176 the three enzymes of the glycolytic pathway that catalyze reactions that are essentially irreversible are also all under all allosteric control. Allosteric enzymes are rarely important in the regulation of metabolic pathways.
Either the enzyme has two distinct active sites or the substrates involved in the two reactions have very similar structures. An allosteric drug may be more specific for specific reaction than one that binds to the receptor itself c. In biochemistry allosteric regulation is the regulation of an enzyme or protein by binding an effector molecule at the proteins allosteric site that is a site other than the proteins active site.
Binding of allosteric regulators alters the conformation of an enzyme. N58-7 Allosteric Regulation of Glycolytic Enzymes by Metabolic Products Pasteur Effect. Which of the following statements about allosteric enzyme regulation are true.
Which of the following is an advantage of an allosteric drug compared to an orthosteric one. Cas9 is an allosteric enzyme which is allosterically regulated in conformational activation target recognition and. Effectors that enhance the proteins activity are referred to as allosteric activators whereas those that decrease the proteins activity are called allosteric inhibitors.
An anabolic steroid b. In competitive the substrate and inhibitor bind at the same active site - pretty straightforward. Allosteric sites allow effectors to bind to the protein often resulting in a conformational change involving protein dynamics.
There are many allosteric enzymes that take part in the biochemical pathways so that the system is well controlled and modulated. The CRISPR-Cas9 system from Streptococcus pyogenes has been exploited as a programmable RNA-guided DNA targeting and editing platform. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins sense the availability of a broad range of small molecules including metal ions metabolites and drugs with the final biological outcome of altering.
The enzyme is composed of at least two subunits. Allosteric regulators are often end products of a biochemical pathway. The enzyme contains α-helices and β-pleated sheets.
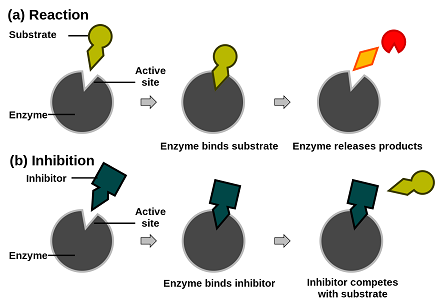
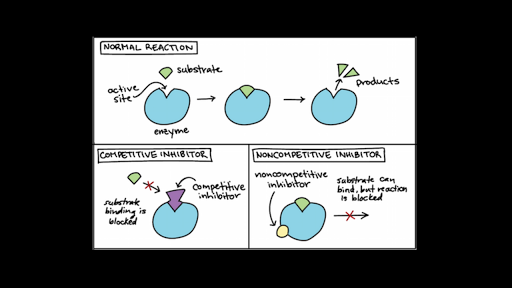
The binding of the sigma subunit to a promoter sequence. A mimic of the substrate competes for the active site. In most cases the binding.
B Coenzymes bind to a protein changing its activity. Explore the process of the allosteric regulation of enzymes and how feedback inhibition. They proposed the following.
Different allosteric regulators turn enzyme activity on or off by binding the same site. I that allostery need not be restricted to end-product inhibition and could be a general form of regulation ii that it might be very difficult to predict the chemical nature of allosteric effectors and therefore to discover them and iii that allosteric sites might be even. In allosteric regulation speaking specifically about inhibition here the inhibitor is binding at a site other than the active site and changing the enzyme in some way to make it inactive.
Which of the following characteristics is not associated with allosteric regulation of an enzymes activity. A DNA helix c. Allosteric regulation is always used to negatively regulate enzyme activity.
Which of the following is an example of allosteric regulation. Aspartate Transcarbamoylase ATCase Cytidine triphosphate CTP is the end product and also inhibits the reaction. The enzyme is subject to competitive inhibition and allosteric regulation.
This evolutionary tool enables diverse genetic manipulations with unprecedented precision and ease. Which of the following statements best describes allosteric regulation. In biochemistry allosteric regulation is the regulation of an enzyme by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzymes active site.
In that it is defined and named from a negative point of view. Allosteric inhibition is designed into the proteins and represents an important physiological process. Diffrent allosteric regulators turn enzyme activity on or off by binding the same site.
C A trace metal binds to an enzyme and a substrate likning the 2 together. Hexokinase in muscle the comparable enzyme in liver is glucokinase catalyzes the essentially irreversible conversion of. The enzyme is subject to competitive inhibition and allosteric regulation.
The binding of the sigma subunit to RNA polymerase C. Allosteric enzyme regulation therefore is when a molecule binds a site other than the active site and changes the behavior of the enzyme by changing its conformation. Either the enzyme has two distinct active sites or the substances involved in the two reactions have very similar structures.
Which of the following is most similar in structure to ATP. Yes but it helps to be more specific. An amino acid with three phosphate groups attached.
Allosteric control of transcriptional regulatory proteins enables organisms to respond to changes in environmental and metabolic conditions. The binding of CAMP-CAP to DNA B. Noncompetitive inhibition is more of a catch-all for non-physiological inhibition that does not compete with substrate for substrate binding to enzyme.
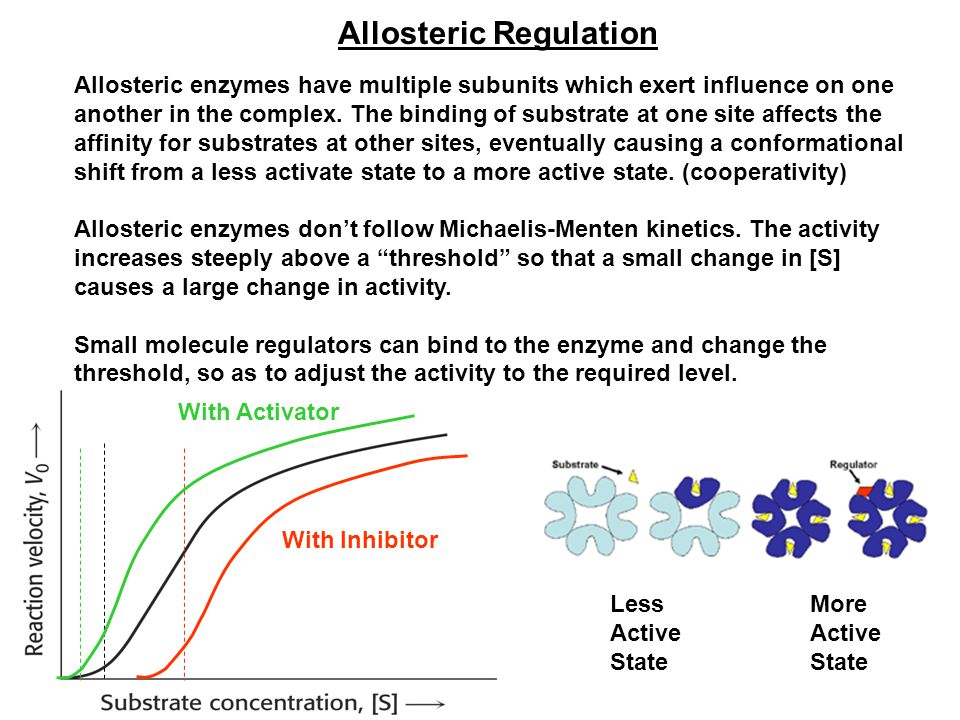
Allosteric regulations is always used to negatively regulate enzyme activity. A Rate of protein synthesis is changed by binding or a regular molecule to the promoter sequence. Allosteric enzymes have a hyperbolic plot of reaction rate vs.
It is known as feedback regulation. Which of the following is true. They can modulate their effect in a more subtle way b.
This first discussion of allosteric enzymes was prescient in many respects. Allosteric regulation is the balance of enzyme activity using specialized molecules that affect the enzymes. Michaelis-Menten kinetics describe the reactions of allosteric enzymes C.
The enzyme contains α-helices and β-pleated sheets.

Enzyme Regulation Article Khan Academy
Allosteric Enzyme Regulation And Covalent Enzyme Modification Tuition Tube
What Is Allosteric Inhibition Quora

Chapter 10 Stacey Flashcards Quizlet

Allosteric Regulations Of Glycolysis Confer Metabolic Plasticity With Download Scientific Diagram

List Of Currently Approved Allosteric Drugs 136 In Alphabetical Order Download Scientific Diagram
Enzyme Regulation Article Khan Academy
Lecture 14 Regulation Of Proteins 1 Allosteric Control Of Atcase Ppt Video Online Download
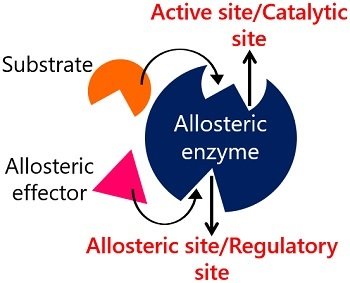
What Is Allosteric Site Definition Features Examples Regulation Biology Reader

What Is The Difference Between Non Competitive And Allosteric Inhibition Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
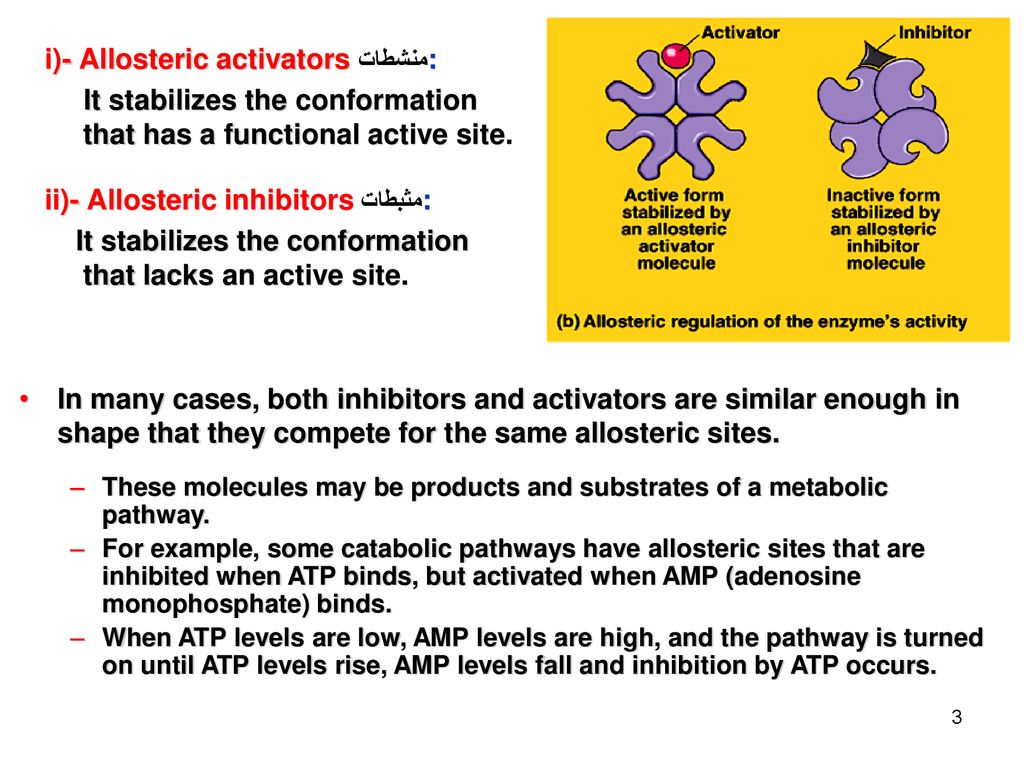
Section C The Control Of Metabolism Ppt Download

Rational Design Of Gpcr Allosteric Regulation A Left And Right B2ar Download Scientific Diagram
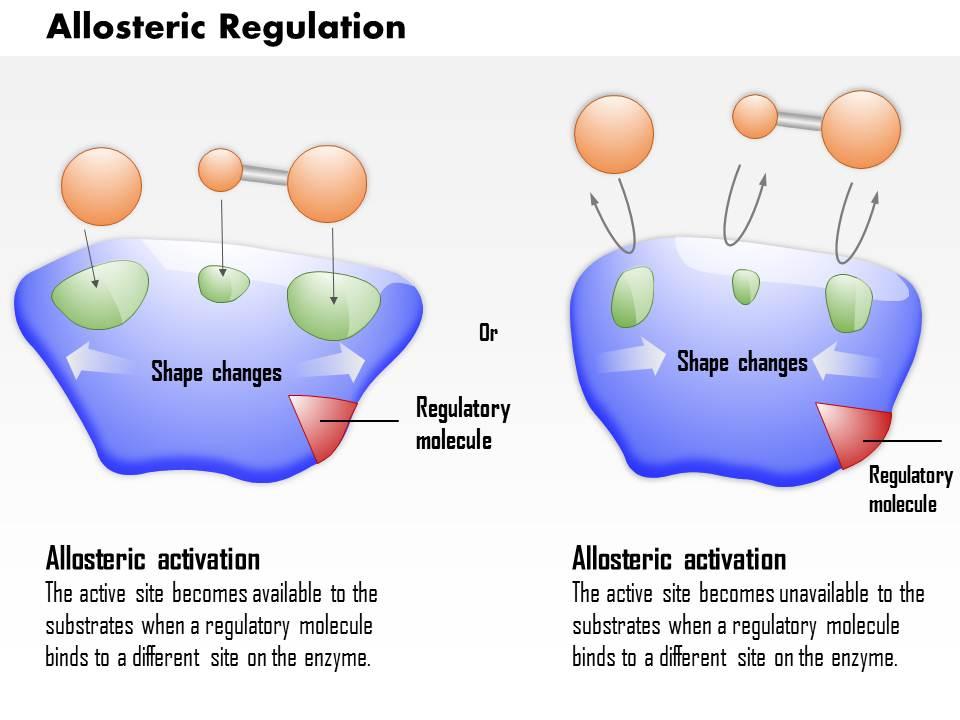
0614 Allosteric Regulation Medical Images For Powerpoint Powerpoint Slide Clipart Example Of Great Ppt Presentations Ppt Graphics

Allosteric Inhibition The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Classical Model For Allosteric Regulation Of Receptor Pam Positive Download Scientific Diagram

Section C The Control Of Metabolism Ppt Download
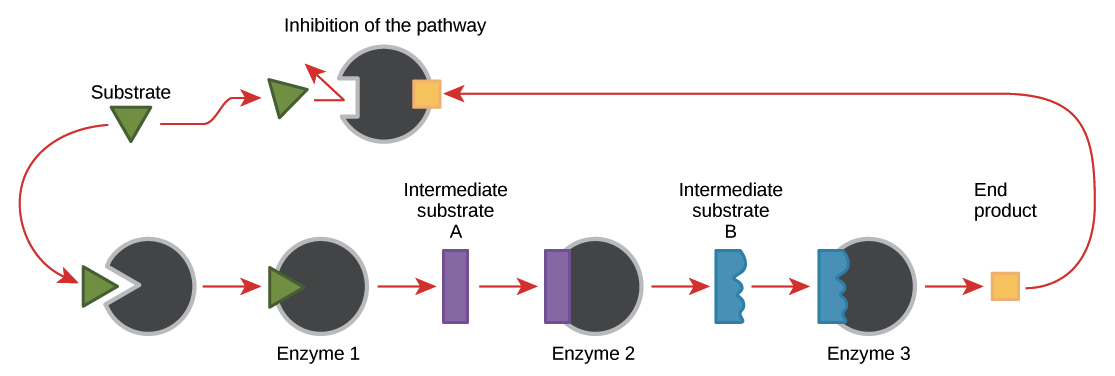
Enzyme Regulation Article Khan Academy
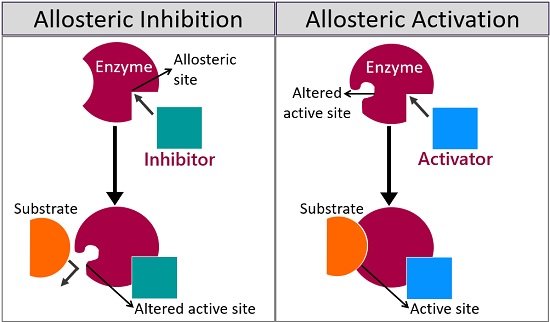
What Is Allosteric Site Definition Features Examples Regulation Biology Reader
Comments
Post a Comment